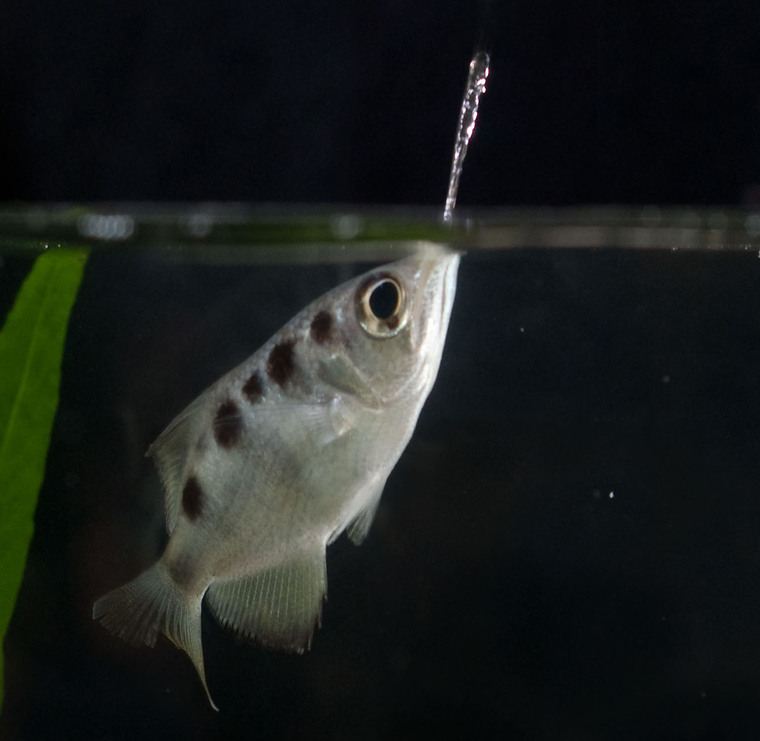
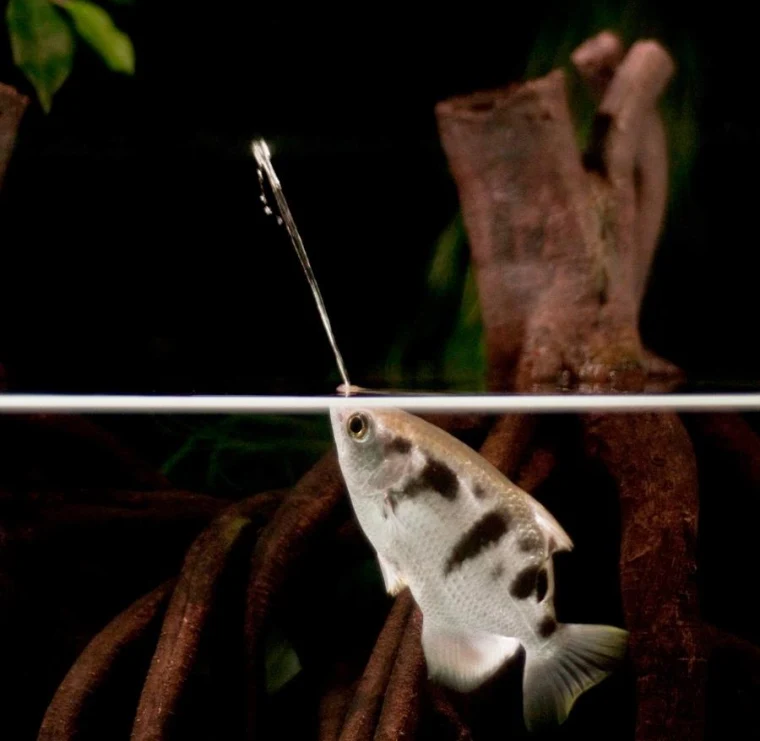
The Banded Archer fish (Toxotes jaculatrix), recognized for its distinctive prey-capturing technique. This species, often caught from the wild, thrives in various freshwater and brackish environments across Southeast Asia and has been categorized as ‘Least Concern’ by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). Banded Archer fish are noted for their remarkable ability to shoot jets of water at aerial prey, a behaviour supported by specialized anatomical adaptations that enable precise targeting and high-speed water propulsion (Hidayah et al., 2023)
1.1. Balanced Diet for Banded Archer Fish
Proper nutrition is crucial for the health of Banded Archer fish (Toxotes jaculatrix) in captivity. These fish are naturally insectivorous but can adapt to a variety of diets in aquarium settings. A balanced diet should include a mix of proteins, fats, and vitamins typically found in their natural prey. It is important to mimic their natural feeding habits to some extent by incorporating floating food items that stimulate their instinct to shoot jets of water to capture food. This not only provides nourishment but also encourages natural behaviour, enhancing their overall well-being in captivity (Gore, 2006).


1.2. Details of the Ingredients in the Diet
The diet for Banded Archer fish should ideally consist of live or frozen foods such as bloodworms, brine shrimp, and small crickets, which provide the necessary protein content. Additionally, formulated floating pellets designed for carnivorous fish can be included to ensure a consistent supply of all essential nutrients. These pellets are often fortified with vitamins and minerals to support health and Vigor in captive fish.
- Protein Sources: The diet should primarily include high-quality fish meal and crustacean meal, which closely mimic the fish’s natural intake of aquatic organisms. Inclusion of insect meal (such as dried crickets or mealworms) can enrich the diet with essential amino acids and fatty acids, vital for growth and health (Halver, 1976).
- Lipid Sources: A blend of fish oil and soybean oil will provide a balanced supply of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, supporting cellular health and reducing inflammation (Turchini et al., 2009).
- Carbohydrate Sources: Limited inclusion of carbohydrates through sources like wheat germ or rice bran is recommended, as it provides energy and aids in the processing of the diet. It’s crucial that the carbohydrates are easily digestible, considering the limited ability of many fish species to metabolize complex carbohydrates efficiently (Wilson, 1994).
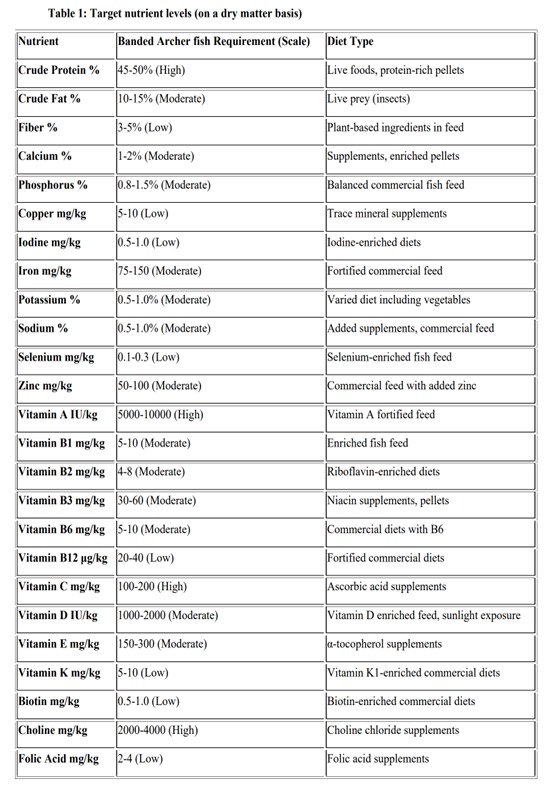
- Vitamins and Minerals: A comprehensive vitamin and mineral mix is essential for the prevention of deficiencies, particularly focusing on vitamins A, D, E, and C, and minerals like zinc and selenium, which play crucial roles in immune function and overall health.
1.3. Analysis of the Nutrient Content
The nutrient profile of the proposed diet should align closely with the fish’s natural intake. In the wild, Banded Archer fish consume a high-protein diet primarily from insects. The recommended captive diet provides protein from both animal and formulated sources, ensuring a balanced intake of amino acids essential for muscle development and maintenance (Islam et al., 2020). The inclusion of live food not only meets their protein needs but also encourages natural foraging and hunting behaviours, which are crucial for their mental health and physical conditioning (Gore, 2006).
1.4. Nutrient Energy Requirements
The diet should be formulated to contain approximately 45-50% protein, 10-15% lipids, and under 10% carbohydrates. This composition ensures a high-protein diet necessary for growth and sustenance, with enough energy to mimic the natural feeding energy expenditure of the species in the wild (Furuya et al., 2004). The specific energy and nutrient content should align with the known requirements for carnivorous fish (Boonyaratpalin et al., 1977), ensuring optimal growth and health maintenance.
1.5. Feeding Schedule
Banded Archer fish should be fed two to three times per day to mimic their natural sporadic feeding pattern and prevent overfeeding. This feeding frequency helps ensure that all food is consumed quickly, reducing waste and maintaining better water quality, which is critical for the health of the fish in captivity. Maintaining such a schedule aligns with established aquaculture practices, supporting better growth performance and feed utilization, thereby fostering a healthy aquarium environment (Zakaria et al., 2016).
1.6. Benefits of the Diet Formulated
The formulated diet benefits the Banded Archer fish by providing a balanced nutritional profile that supports health, growth, and coloration while also engaging their natural behaviours. Regular feeding of live or mimicking prey items like floating pellets encourages the fish to practice their unique hunting skills, which is vital for their cognitive development and stress reduction in a captive environment (Islam et al., 2020)

1.7. Ease of Management of the Diet
- The diet for Banded Archerfish can be managed effectively by incorporating a mix of commercially available fish pellets, frozen or live foods, and vegetables, ensuring both nutritional balance and cost-effectiveness (Charo-Karisa et al., 2013).
- Furthermore, these ingredients are generally readily available in most pet stores or aquatic supply shops, making it convenient for aquarium owners to obtain the necessary components for maintaining a consistent diet for Banded Archerfish.
- In terms of storage, most components of the diet, such as fish pellets and frozen foods, can be easily stored for extended periods if kept in a freezer or refrigerator, which helps in maintaining the quality and freshness of the ingredients.
- The preparation time of the diet involves minimal effort; simple processes such as thawing frozen foods and rinsing live foods before feeding are quick and ensure the fish receive fresh, nutritious meals without excessive preparation time.
1.8. Considerations when Formulating their Diet
- Food Acquisition Techniques: Banded Archer fish uniquely use water jets to dislodge insects, suggesting the need for surface-floating foods to mimic this behavior. Recommended are floating pellets to maintain natural hunting practices (Das et al., 2014).
- Digestive System Adaptability: The digestive tract of Banded Archer fish handles diverse foods, from insects to small fish. A varied diet, including different protein sources, replicates gut transit times akin to their wild counterparts, enhancing nutrient uptake (Das et al., 2014).
- Replication of Natural Diet: In nature, these fish predominantly eat live prey like insects and small aquatic creatures. In captivity, combining live food (example; brine shrimp) with floating, high-quality pellets encourages natural feeding patterns and ensures balanced nutrition.
- Feeding Schedule Considerations: Mimicking the sporadic feeding habits seen in the wild, Banded Archer fish in captivity benefit from small, frequent feedings rather than large, single meals to prevent overfeeding and related health issues.
- Energy Needs Variation: Depending on their life stage and activity level, Banded Archer fish’s energy requirements change. Juveniles and pregnant females, for instance, need more protein-rich diets to support growth and reproduction. Seasonal changes in environment like water temperature and lighting also influence their metabolic needs.
- Practical Diet Formulation: While striving to emulate their natural diet, factors such as cost, ingredient availability, and storage must be considered. Using commercially available fish foods supplemented with occasional live treats offers a viable feeding strategy.



